- Posts: 36
- Thank you received: 2
- Forum
- Technical Divisions
- Fiber optic
- What is WDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexer) and how does it work?
×
Questions regarding all aspects of Fiber Optics manufacturing and production go here.
What is WDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexer) and how does it work?
- Mrs Bella Tse
- Topic Author
- Offline
- Junior Boarder
-
Less
More
2 years 2 weeks ago #3228
by Mrs Bella Tse
What is WDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexer) and how does it work? was created by Mrs Bella Tse
As technology continues to advance, the demand for more data and faster speeds increases. One way to meet these demands is by using Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology, which allows for the expansion of a network's capacity by increasing the amount of data that can be transmitted over a single fiber optic cable. In this article, we'll explore how WDM works and the benefits it can bring to your network.
What is WDM ?
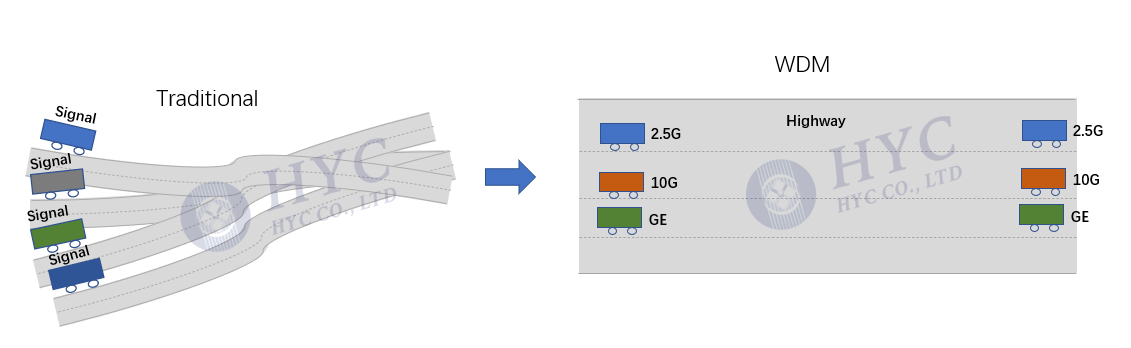
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technology that allows multiple signals to be transmitted over a single fiber optic cable by using different wavelengths (colors) of light. The different wavelengths are separated and then combined again at the receiving end. This means that multiple data streams can be sent over the same fiber optic cable at the same time, without interfering with each other.
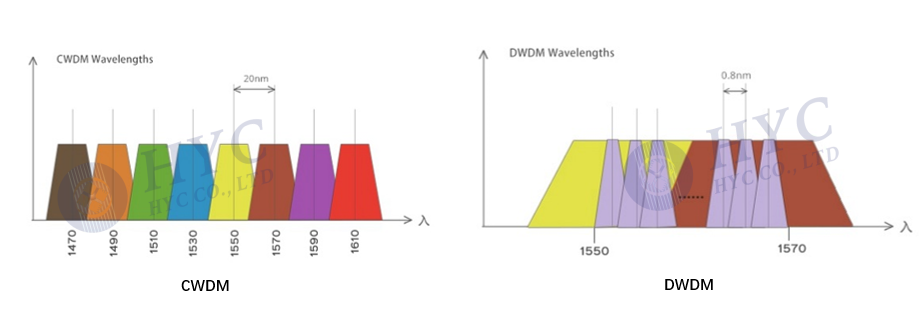
There are two main types of WDM: Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM). CWDM uses a wider wavelength range and is generally used for shorter distances, while DWDM uses a narrower wavelength range and is used for longer distances.
The most difference between CWDM and DWDM is the spacing of wavelength which causes the number of wavelength or channels that can be used. That's the difference between “Coast” and “Dense”. CWDM channels each consume 20 nm channel spacing from 1470 to 1610 nm, it's typically deployed on fiber spans up to 80km or less because optical amplifiers cannot be used with large spacing channels. Instead of the 20 nm spacing in CWDM, DWDM uses either 50, 100 or 200 GHz spacing which allows many more wavelengths to be packed onto the same fiber. The common channels of CWDM are 8 to 18, while DWDM can carry 40, 80 or even up to 160 wavelengths, which is suitable for long-reach communications up to 120 km and beyond. Today's DWDM systems typically support 96 channels spaced at 0.8 nm apart within the 1550 nm C-Band spectrum. With the help of EDFA, DWDM system can work in the distance of thousands of kilometers.
How does WDM work?
WDM works by using multiple lasers, each emitting a different color of light, to transmit data over a single fiber optic cable. The light signals are then combined and sent down the fiber optic cable. At the receiving end, the signals are separated using a demultiplexer and then converted back into their original form.
WDM allows for multiple data streams to be sent over a single fiber optic cable at the same time, without interfering with each other. This means that more data can be transmitted in less time, which increases the capacity of the network.
Benefits of using WDM
The use of WDM technology brings several benefits to a network, including:
Increased capacity: By allowing multiple data streams to be sent over a single fiber optic cable at the same time, WDM increases the capacity of the network. This means that more data can be transmitted in less time, which can help to improve the overall performance of the network.
Cost savings: Using WDM technology can help to reduce the number of fiber optic cables needed to transmit data, which can lead to cost savings. This is because fewer cables need to be installed, maintained, and upgraded, which can reduce the overall cost of the network.
Improved reliability: WDM technology can help to improve the reliability of the network by reducing the risk of signal interference. By separating the different data streams using different wavelengths of light, WDM ensures that the signals do not interfere with each other, which can help to improve the overall reliability of the network.
Scalability: WDM technology is scalable, which means that it can be easily expanded as the needs of the network grow. This makes it a flexible and future-proof technology that can adapt to the changing demands of the network.
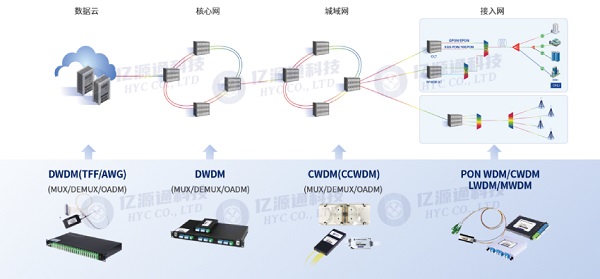
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology has a wide range of applications in various industries. Let's take a look at some of the specific examples:
Telecommunications: WDM is commonly used in telecommunications networks to increase the capacity of fiber optic cables. This allows telecommunications companies to transmit more data over their networks, which is critical for delivering high-speed internet, voice, and video services. For example, a single fiber optic cable using DWDM technology can transmit up to 80 channels, each carrying a data rate of up to 100 Gbps, resulting in a total capacity of 8 Tbps.
Data Centers: WDM technology is also used in data centers to increase the capacity of their fiber optic connections. By using WDM, data centers can transmit more data over their fiber optic cables, which helps to improve the performance of cloud computing, online gaming, and other high-bandwidth applications.
Military: WDM technology is used in military communications to improve the security and reliability of their networks. By using different wavelengths of light to transmit different data streams, WDM helps to prevent interference and eavesdropping, which is critical for military operations.
Medical Imaging: WDM technology is also used in medical imaging applications, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans. By using WDM, medical professionals can transmit large amounts of data quickly and efficiently, which is critical for timely diagnoses and treatments.
Cable TV: WDM technology is used in cable TV networks to increase the number of channels that can be transmitted over a single fiber optic cable. This helps to improve the quality of the TV signal and reduce the number of cables needed to transmit the signal.
Overall, the applications of WDM technology are vast and varied, and its use is critical for improving the capacity, reliability, and efficiency of many different types of networks.
Conclusion
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology is a powerful tool for expanding the capacity of a network. By allowing multiple data streams to be sent over a single fiber optic cable at the same time, WDM can increase the capacity of the network, reduce costs, improve reliability, and provide scalability. As technology continues to advance and the demand for more data and faster speeds increases, WDM will play an increasingly important role in meeting these demands.
ABOUT HYC
With more than 20 years’ experience of WDM manufacturing, HYC can provide full series of WDM products, including CWDM, DWDM, FWDM, CCWDM, etc.
For more information:
What is WDM ?
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technology that allows multiple signals to be transmitted over a single fiber optic cable by using different wavelengths (colors) of light. The different wavelengths are separated and then combined again at the receiving end. This means that multiple data streams can be sent over the same fiber optic cable at the same time, without interfering with each other.
There are two main types of WDM: Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM). CWDM uses a wider wavelength range and is generally used for shorter distances, while DWDM uses a narrower wavelength range and is used for longer distances.
The most difference between CWDM and DWDM is the spacing of wavelength which causes the number of wavelength or channels that can be used. That's the difference between “Coast” and “Dense”. CWDM channels each consume 20 nm channel spacing from 1470 to 1610 nm, it's typically deployed on fiber spans up to 80km or less because optical amplifiers cannot be used with large spacing channels. Instead of the 20 nm spacing in CWDM, DWDM uses either 50, 100 or 200 GHz spacing which allows many more wavelengths to be packed onto the same fiber. The common channels of CWDM are 8 to 18, while DWDM can carry 40, 80 or even up to 160 wavelengths, which is suitable for long-reach communications up to 120 km and beyond. Today's DWDM systems typically support 96 channels spaced at 0.8 nm apart within the 1550 nm C-Band spectrum. With the help of EDFA, DWDM system can work in the distance of thousands of kilometers.
How does WDM work?
WDM works by using multiple lasers, each emitting a different color of light, to transmit data over a single fiber optic cable. The light signals are then combined and sent down the fiber optic cable. At the receiving end, the signals are separated using a demultiplexer and then converted back into their original form.
WDM allows for multiple data streams to be sent over a single fiber optic cable at the same time, without interfering with each other. This means that more data can be transmitted in less time, which increases the capacity of the network.
Benefits of using WDM
The use of WDM technology brings several benefits to a network, including:
Increased capacity: By allowing multiple data streams to be sent over a single fiber optic cable at the same time, WDM increases the capacity of the network. This means that more data can be transmitted in less time, which can help to improve the overall performance of the network.
Cost savings: Using WDM technology can help to reduce the number of fiber optic cables needed to transmit data, which can lead to cost savings. This is because fewer cables need to be installed, maintained, and upgraded, which can reduce the overall cost of the network.
Improved reliability: WDM technology can help to improve the reliability of the network by reducing the risk of signal interference. By separating the different data streams using different wavelengths of light, WDM ensures that the signals do not interfere with each other, which can help to improve the overall reliability of the network.
Scalability: WDM technology is scalable, which means that it can be easily expanded as the needs of the network grow. This makes it a flexible and future-proof technology that can adapt to the changing demands of the network.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology has a wide range of applications in various industries. Let's take a look at some of the specific examples:
Telecommunications: WDM is commonly used in telecommunications networks to increase the capacity of fiber optic cables. This allows telecommunications companies to transmit more data over their networks, which is critical for delivering high-speed internet, voice, and video services. For example, a single fiber optic cable using DWDM technology can transmit up to 80 channels, each carrying a data rate of up to 100 Gbps, resulting in a total capacity of 8 Tbps.
Data Centers: WDM technology is also used in data centers to increase the capacity of their fiber optic connections. By using WDM, data centers can transmit more data over their fiber optic cables, which helps to improve the performance of cloud computing, online gaming, and other high-bandwidth applications.
Military: WDM technology is used in military communications to improve the security and reliability of their networks. By using different wavelengths of light to transmit different data streams, WDM helps to prevent interference and eavesdropping, which is critical for military operations.
Medical Imaging: WDM technology is also used in medical imaging applications, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans. By using WDM, medical professionals can transmit large amounts of data quickly and efficiently, which is critical for timely diagnoses and treatments.
Cable TV: WDM technology is used in cable TV networks to increase the number of channels that can be transmitted over a single fiber optic cable. This helps to improve the quality of the TV signal and reduce the number of cables needed to transmit the signal.
Overall, the applications of WDM technology are vast and varied, and its use is critical for improving the capacity, reliability, and efficiency of many different types of networks.
Conclusion
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology is a powerful tool for expanding the capacity of a network. By allowing multiple data streams to be sent over a single fiber optic cable at the same time, WDM can increase the capacity of the network, reduce costs, improve reliability, and provide scalability. As technology continues to advance and the demand for more data and faster speeds increases, WDM will play an increasingly important role in meeting these demands.
ABOUT HYC
With more than 20 years’ experience of WDM manufacturing, HYC can provide full series of WDM products, including CWDM, DWDM, FWDM, CCWDM, etc.
For more information:
Please Log in to join the conversation.
Moderators: Erik A Macs, Peter J Stewart-Hay
- Forum
- Technical Divisions
- Fiber optic
- What is WDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexer) and how does it work?
Time to create page: 0.060 seconds




 How to resolve AdBlock issue?
How to resolve AdBlock issue?